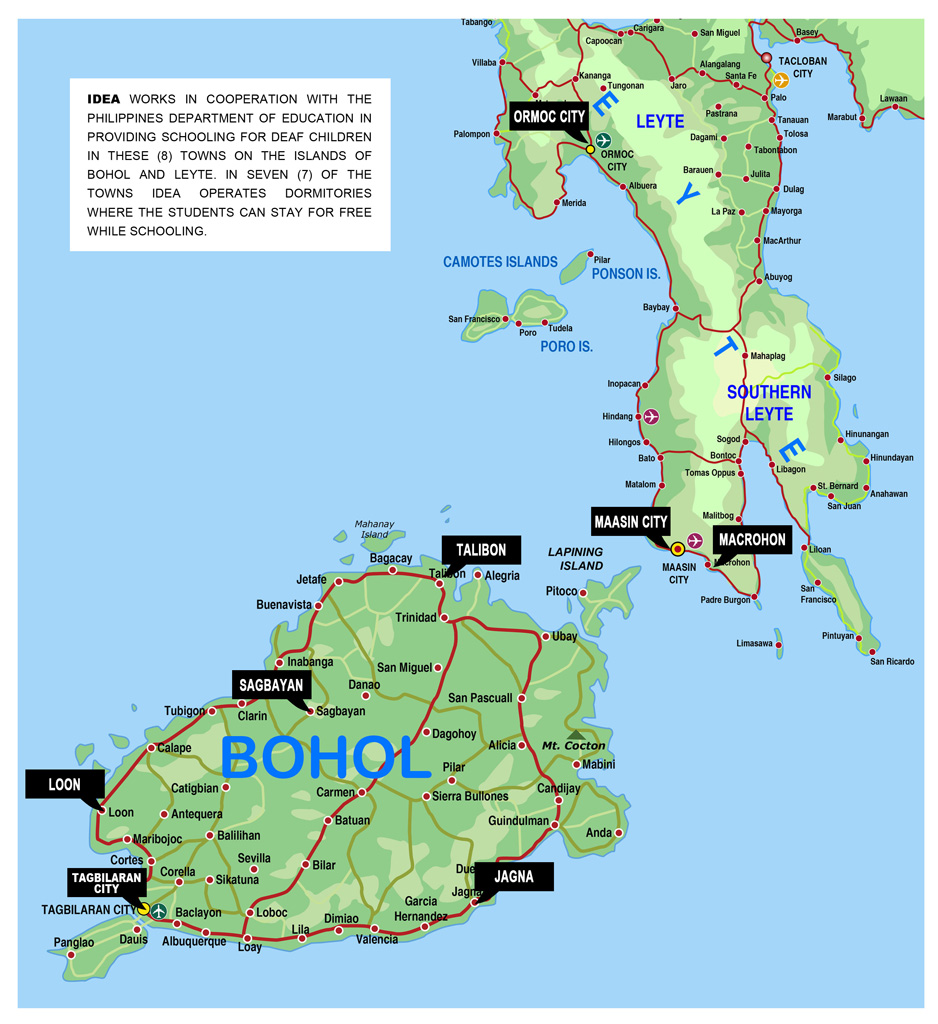
Although there are tens of thousands of deaf children and adults in the Philippines, IDEA is currently focusing its effort on the islands of Bohol and Leyte in the center of the archipelago.
PROVINCE OF BOHOL
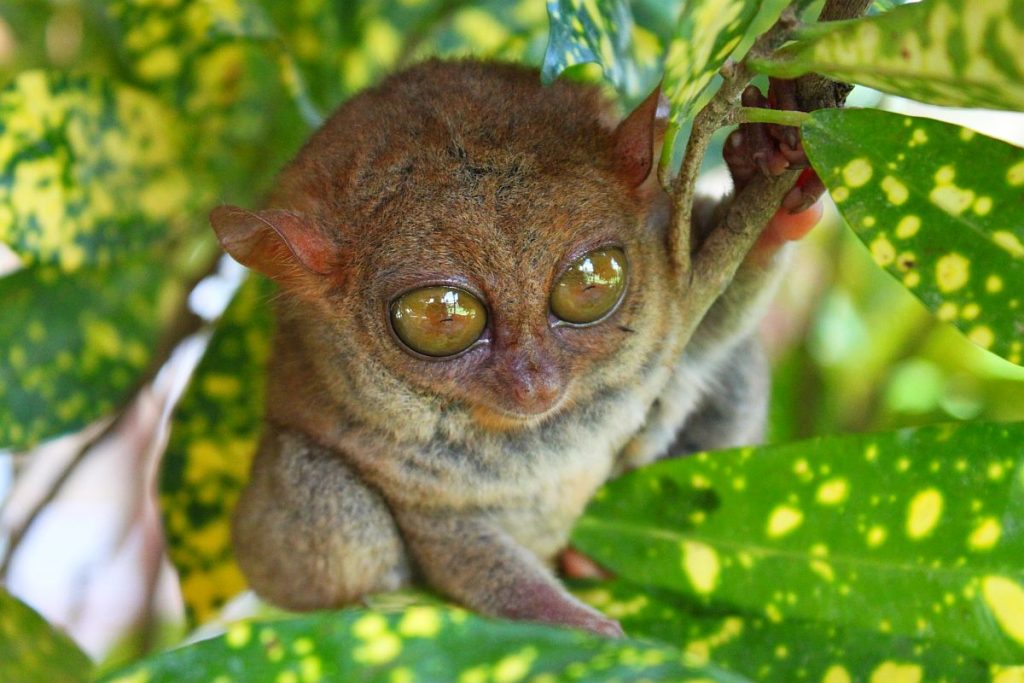



The Philippine Tarsier, considered the second-smallest primate in the world, is indigenous to the island.
Bohol is a first class island province of the Philippines located in the Central Visayas region, consisting of Bohol Island and 75 minor surrounding islands. Its capital is Tagbilaran City. With a land area of 4,117.26 square kilometers (1,589.68 sq mi) and a coastline 261 kilometers (162 mi) long, Bohol is the tenth largest island of the Philippines. To the west of Bohol is Cebu, to the northeast is the island of Leyte and to the south, across the Bohol Sea is Mindanao.
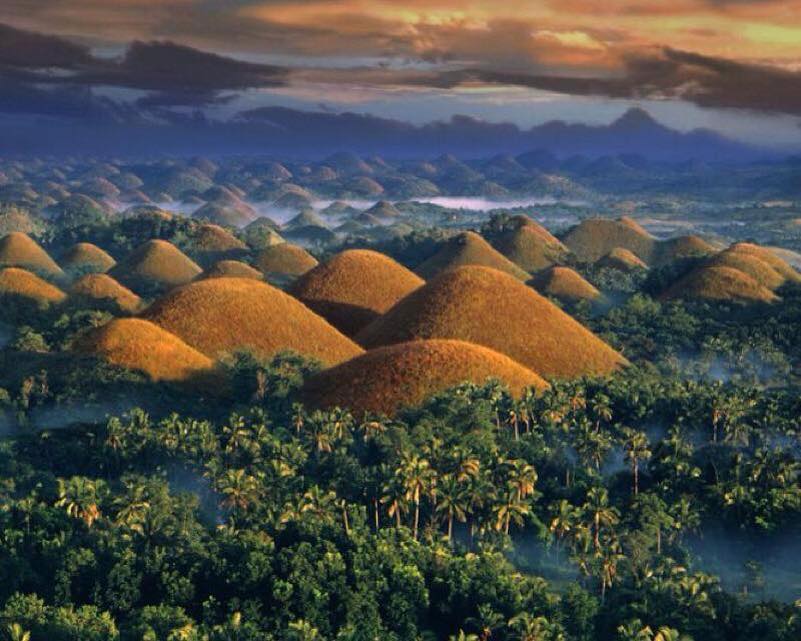
The province is a popular tourist destination with its beaches and resorts. The Chocolate Hills, numerous mounds of limestone formation, is the most popular attraction. Panglao Island, located just southwest of Tagbilaran City, is famous for its diving locations and routinely listed as one of the top ten diving locations in the world. Numerous tourist resorts dot the southern beaches and cater to divers from around the world. The Philippine Tarsier, considered the second-smallest primate in the world, is indigenous to the island.
The Chocolate Hills is an unusual geological formation in Bohol Province, Philippines. There are at least 1,260 hills but there may be as many as 1,776 hills spread over an area of more than 50 square kilometers (20 sq mi). They are covered in green grass that turns brown during the dry season. This transforms the area into seemingly endless rows of “chocolate kisses”.The Chocolate Hills is a famous tourist attraction of Bohol, scattered by the hundreds throughout the towns of Carmen, Batuan and Sagbayan in Bohol. They are featured in the provincial flag and seal to symbolize the abundance of natural attractions in the province.They are in the Philippine Tourism Authority’s list of tourist destinations in the Philippines;they have been declared the country’s third National Geological Monument and proposed for inclusion in the UNESCO World Heritage List.
PROVINCES OF NORTHERN AND SOUTHERN LEYTE
Leyte is an island in the Visayas group of the Philippines.
The island measures about 180 km (110 mi) north-south and about 65 km (40 mi) at its widest point. In the north it nearly joins Samar, separated by the San Juanico Strait, which becomes as narrow as 2 km (1.2 mi) in some places. The island province of Biliran is also to the north of Leyte and is joined to Leyte island by a bridge across the narrow Biliran Strait. To the south Leyte is separated from Mindanao by the Surigao Strait. To the east, Leyte is somewhat “set back” from the Philippine Sea of the Pacific Ocean, Samar to the northeast and Dinagat to the southeast forming the Leyte Gulf. To the west are Cebu and Bohol.
Leyte is mostly heavily forested and mountainous, but the Leyte Valley in the northeast has much agriculture.
Politically, the island is divided into two provinces: (Northern) Leyte and Southern Leyte. Territorially, Southern Leyte Province includes the island of Panaon to its south. Biliran Island, to the north of Leyte Island, was formerly a sub-province of Leyte, and is now a separate province, Biliran Province.
The chief cities of Leyte are Tacloban City, on the eastern shore at the northwest corner of Leyte Gulf, and Ormoc City, on the west coast.
